On an upper-level chart the wind tends to blow – On upper-level charts, the wind tends to blow in a predictable manner, providing valuable insights into weather patterns and climate systems. Meteorologists rely on these charts to make accurate weather forecasts and understand the dynamics of the atmosphere.
Upper-level charts depict wind patterns at high altitudes, typically above 20,000 feet. By analyzing these charts, meteorologists can identify jet streams, areas of strong winds that significantly influence weather systems and climate patterns.
1. Introduction
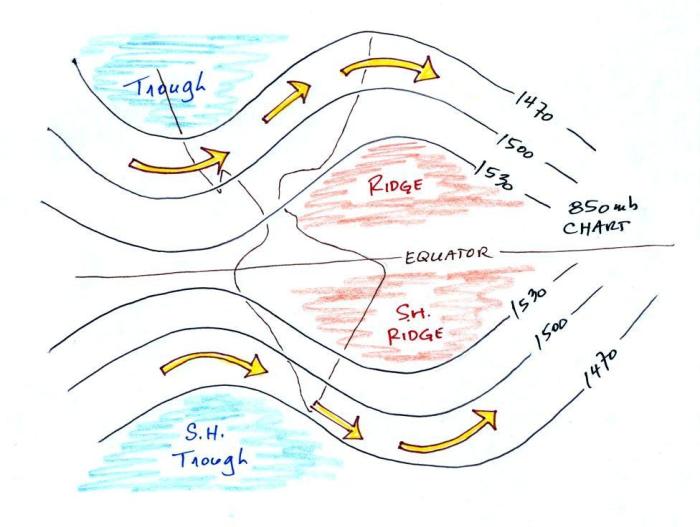
Upper-level charts are essential tools in meteorology, providing a comprehensive view of the wind patterns and atmospheric conditions at high altitudes. These charts are used extensively in weather forecasting and play a crucial role in predicting weather systems and climate patterns.
Examples of upper-level charts include constant pressure charts and isobaric charts, which depict wind patterns at specific pressure levels in the atmosphere.
2. Wind Patterns on Upper-Level Charts: On An Upper-level Chart The Wind Tends To Blow
Upper-level charts reveal distinct wind patterns that vary with altitude. Generally, winds tend to blow from west to east in the mid-latitudes, a phenomenon known as the prevailing westerlies.
Factors influencing wind direction and speed at different levels include the Coriolis effect, pressure gradients, and temperature differences.
3. Jet Streams and Upper-Level Winds
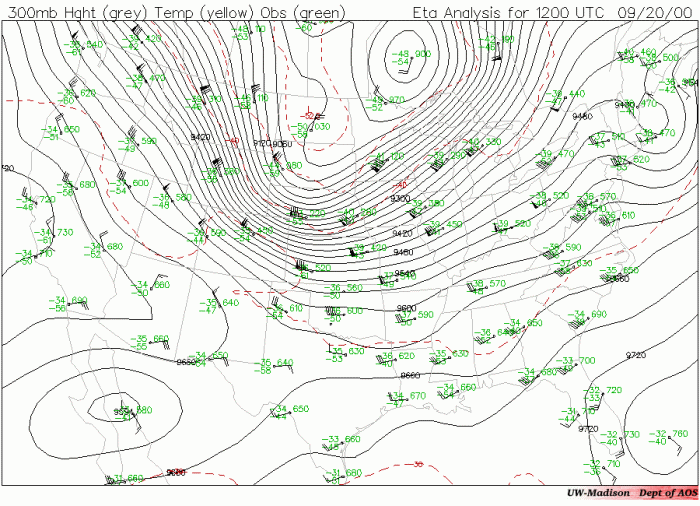
Jet streams are narrow, fast-flowing air currents in the upper atmosphere that significantly impact wind patterns on upper-level charts.
Jet streams affect weather systems by steering cyclones and anticyclones, influencing precipitation patterns and climate variability.
4. Applications of Upper-Level Wind Analysis
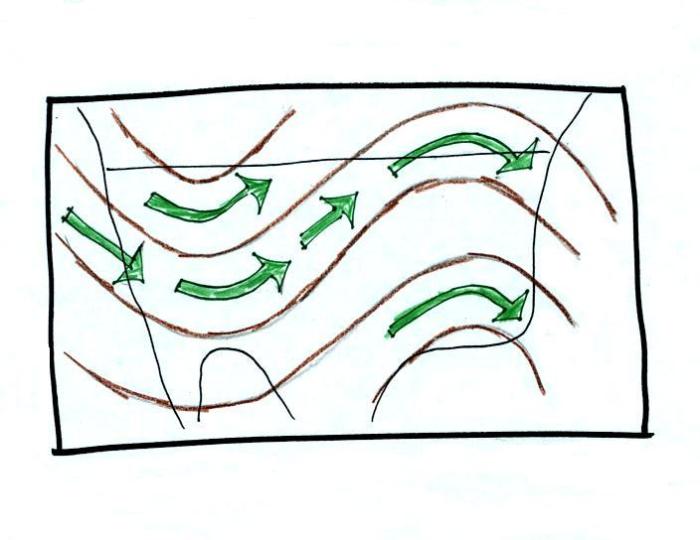
Meteorologists utilize upper-level wind analysis to forecast weather patterns and predict the movement of weather systems.
Upper-level wind analysis is also employed in aviation to optimize flight routes and in other industries, such as energy and agriculture, to inform decision-making.
5. Limitations and Challenges
While upper-level wind analysis is a valuable tool, it has limitations. Accuracy can be affected by data gaps and uncertainties in measurements.
Meteorologists face challenges in interpreting upper-level wind data due to the complexity of atmospheric processes and the need for specialized knowledge and expertise.
Detailed FAQs
What are upper-level charts?
Upper-level charts are meteorological charts that depict wind patterns at high altitudes, typically above 20,000 feet.
How do meteorologists use upper-level wind analysis?
Meteorologists use upper-level wind analysis to predict weather patterns, track jet streams, and understand the dynamics of the atmosphere.
What is the role of jet streams in wind patterns?
Jet streams are narrow bands of strong winds that significantly influence weather systems and climate patterns. They can transport heat and moisture across vast distances and affect the formation of storms.