Unit 1 Exploring One-Variable Data Answer Key embarks on a comprehensive journey into the realm of data analysis, unveiling the fundamental concepts and techniques for understanding and interpreting data. This guide provides a thorough exploration of data collection methods, organization, display, and statistical measures, empowering readers to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Delving into the intricacies of data analysis, this guide unravels the complexities of measures of central tendency and variability, equipping readers with the knowledge to summarize and describe data effectively. Furthermore, it sheds light on the principles of probability and sampling, enabling readers to draw meaningful conclusions from data and make informed inferences about larger populations.
1. Understanding the Concept of Unit 1 Exploring One-Variable Data
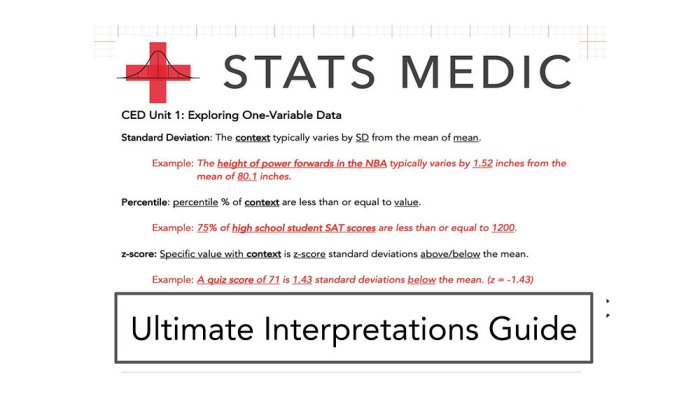
Unit 1 of Exploring One-Variable Data introduces students to the fundamental concepts of data analysis. It emphasizes the importance of data collection, organization, and analysis in making informed decisions.
Key concepts covered in the unit include:
- Data collection methods (surveys, experiments, observations)
- Data organization and display (tables, graphs, charts)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of variability (range, variance, standard deviation)
2. Exploring Data Collection Methods
Data collection is the process of gathering information to answer research questions or gain insights. Different data collection methods have their advantages and disadvantages:
- Surveys:Structured questionnaires used to collect data from a sample of respondents. Advantages: high response rate, easy to analyze. Disadvantages: potential for bias, social desirability bias.
- Experiments:Controlled studies where researchers manipulate variables to observe their effects. Advantages: high internal validity, causal inferences can be made. Disadvantages: expensive, time-consuming, artificial settings.
- Observations:Recording data about individuals or groups in their natural settings. Advantages: high ecological validity, unobtrusive. Disadvantages: potential for observer bias, difficulty in generalizing findings.
Ethical considerations in data collection include informed consent, confidentiality, and privacy.
3. Organizing and Displaying Data, Unit 1 exploring one-variable data answer key
Organizing and displaying data effectively helps researchers understand patterns and trends. Common data displays include:
- Tables:Organize data in rows and columns, allowing for easy comparisons and sorting.
- Graphs:Visual representations of data using lines, bars, or points. Different types of graphs are suitable for different types of data.
- Charts:Circular or pie-shaped diagrams that show the proportions of different categories.
The choice of data display depends on the type of data, the purpose of the analysis, and the audience.
4. Measures of Central Tendency
Measures of central tendency describe the “average” value of a data set:
- Mean:Sum of all values divided by the number of values. Sensitive to outliers.
- Median:Middle value when data is arranged in order from smallest to largest. Not affected by outliers.
- Mode:Value that occurs most frequently. Can be multiple modes.
The appropriate measure of central tendency depends on the shape of the data distribution and the research question.
5. Measures of Variability
Measures of variability describe how spread out a data set is:
- Range:Difference between the largest and smallest values.
- Variance:Average squared difference between each value and the mean. Sensitive to outliers.
- Standard deviation:Square root of the variance. Measures the typical distance from the mean.
Measures of variability provide insights into the consistency and homogeneity of a data set.
Questions Often Asked: Unit 1 Exploring One-variable Data Answer Key
What is the purpose of Unit 1 Exploring One-Variable Data?
Unit 1 Exploring One-Variable Data provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts and techniques of data analysis, enabling readers to understand, interpret, and make informed decisions based on data.
What are the key concepts covered in Unit 1?
Unit 1 covers a wide range of key concepts, including data collection methods, data organization and display, measures of central tendency and variability, probability, and sampling.
How can I use this guide to improve my data analysis skills?
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to data analysis, offering clear explanations, practical examples, and exercises to help readers develop their skills and gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter.

