Lesson 1 truman and eisenhower – Lesson 1: Truman and Eisenhower sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This lesson delves into the presidencies of Harry S.
Truman and Dwight D. Eisenhower, two pivotal figures who shaped the course of American history during and after World War II.
Their domestic and foreign policies, leadership styles, and political legacies will be examined, providing a comprehensive understanding of their impact on American society and the world.
Historical Context: Lesson 1 Truman And Eisenhower
The presidencies of Harry S. Truman and Dwight D. Eisenhower spanned a transformative period in American history. The end of World War II marked the beginning of a new era, characterized by the Cold War, the rise of the United States as a global superpower, and significant social and economic changes.
Truman assumed office in 1945 after the sudden death of Franklin D. Roosevelt. He inherited the daunting task of leading the nation through the final stages of the war and its aftermath. The post-war years were marked by economic uncertainty, labor unrest, and the escalating tensions with the Soviet Union.
Cold War, Lesson 1 truman and eisenhower
The Cold War, a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, dominated the international landscape during the Truman and Eisenhower presidencies. The ideological differences between the two superpowers, combined with the development of nuclear weapons, created a climate of fear and mistrust.
Domestic Policies

President Truman’s Fair Deal and President Eisenhower’s Modern Republicanism were two distinct domestic policy agendas that shaped the United States in the post-World War II era. Truman’s Fair Deal aimed to expand the New Deal’s social welfare programs, while Eisenhower’s Modern Republicanism focused on economic growth and limited government intervention.
One of the key differences between the two policies was their approach to social welfare. Truman’s Fair Deal proposed expanding Social Security, providing national health insurance, and increasing the minimum wage. Eisenhower, on the other hand, believed that the private sector was better equipped to handle social welfare programs and favored tax cuts and deregulation.
Economic Policies
In terms of economic policies, Truman’s Fair Deal emphasized government intervention to promote economic growth and stability. Eisenhower’s Modern Republicanism, on the other hand, favored a more hands-off approach, believing that the free market would lead to economic prosperity.
Foreign Policies

The foreign policies of Presidents Truman and Eisenhower reflected the evolving global landscape during their presidencies. Truman’s “containment policy” aimed to prevent the spread of communism, while Eisenhower’s “New Look” strategy focused on nuclear deterrence and alliances.
Truman’s Containment Policy
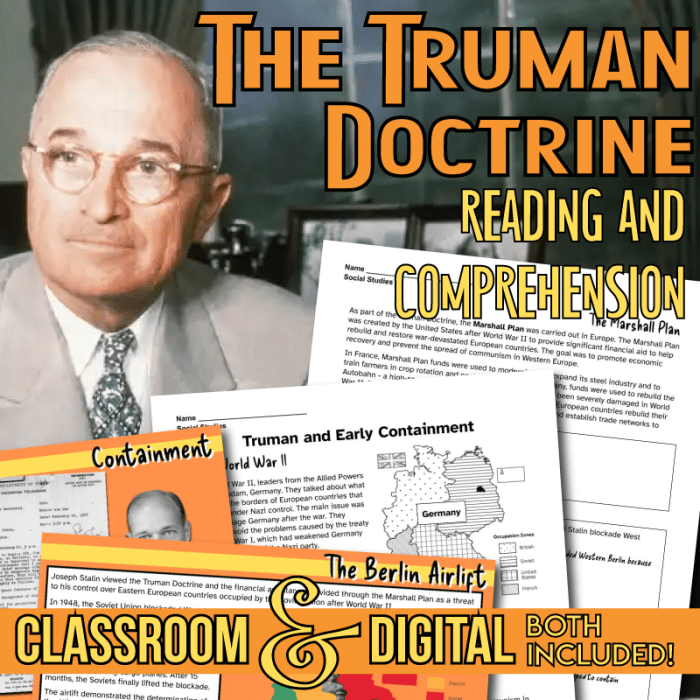
In the aftermath of World War II, the United States emerged as a global superpower. However, the Soviet Union’s expansionist ambitions threatened American interests. Truman’s containment policy sought to halt the spread of communism by providing economic and military aid to countries at risk of falling under Soviet influence.
The policy was most notably implemented in Europe through the Marshall Plan and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
Eisenhower’s “New Look”
Eisenhower’s “New Look” strategy shifted the focus of American foreign policy towards nuclear deterrence. Believing that the United States could not afford to engage in protracted conventional wars, Eisenhower emphasized the development of nuclear weapons and a strong military alliance system.
The first lesson covered Truman and Eisenhower’s presidencies, providing a solid foundation for understanding their impact on American history. For further exploration, I recommend checking out the rn vati medical surgical 2019 resource. Returning to our lesson, Truman and Eisenhower faced distinct challenges and made significant contributions, shaping the post-World War II era.
The strategy was designed to deter potential Soviet aggression by threatening massive nuclear retaliation.
Evolution of US Foreign Policy
Truman’s containment policy and Eisenhower’s “New Look” represented a significant evolution in US foreign policy. Truman’s policy focused on preventing the spread of communism through economic and military assistance, while Eisenhower’s strategy relied heavily on nuclear deterrence and alliances. This shift reflected the changing global dynamics and the growing threat posed by the Soviet Union.
Successes and Failures
Both Truman’s containment policy and Eisenhower’s “New Look” had their successes and failures. Truman’s policy successfully prevented the spread of communism in Western Europe and contained Soviet expansionism. However, it also led to increased tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union and the outbreak of the Korean War.
Eisenhower’s “New Look” strategy deterred Soviet aggression and maintained the nuclear peace, but it also led to an arms race and increased tensions between the two superpowers.
Leadership Styles

Truman and Eisenhower exhibited distinct leadership styles that shaped their presidencies. Truman’s assertive and decisive approach contrasted with Eisenhower’s collaborative and consensus-building style.
Truman’s Decisive Leadership
Harry Truman’s leadership style was characterized by his decisiveness and assertiveness. He was known for his ability to make quick decisions and stick to them, even in the face of opposition. This decisiveness was evident in his handling of the Berlin Airlift and the Korean War.
Eisenhower’s Collaborative Approach
Dwight Eisenhower, in contrast, adopted a more collaborative and consensus-building approach to leadership. He valued teamwork and sought input from his advisors and cabinet members before making decisions. This approach contributed to the stability and prosperity of his presidency.
Comparison and Effectiveness
While Truman’s decisive leadership was effective in handling immediate crises, Eisenhower’s collaborative approach fostered long-term stability and consensus. Both styles had their strengths and weaknesses, and their effectiveness depended on the specific challenges faced during their presidencies.
Political Impact

Truman’s presidency was marked by significant unpopularity, while Eisenhower enjoyed widespread popularity. Several factors contributed to this contrast.
Truman’s Unpopularity
- The Korean War: The Korean War was unpopular among the American public, and Truman was blamed for its escalation.
- Economic problems: The postwar economy was plagued by inflation and labor unrest, which further eroded Truman’s popularity.
- Personal qualities: Truman was often seen as aloof and uncharismatic, which did not help his public image.
Eisenhower’s Popularity
- The Korean War: Eisenhower was able to end the Korean War, which boosted his popularity.
- Economic prosperity: The postwar economy flourished under Eisenhower, which helped to create a sense of optimism and well-being.
- Personal qualities: Eisenhower was a charismatic and likeable figure, which made him popular with the American public.
Legacy on American Politics
Truman’s presidency is often seen as a turning point in American politics. His Fair Deal program marked a significant expansion of the role of the federal government in social welfare, and his foreign policy helped to shape the Cold War.
Eisenhower’s presidency, on the other hand, is often seen as a period of conservatism and consolidation. He reduced the size of the federal government and focused on economic growth.
FAQ Section
What were the key differences between Truman’s Fair Deal and Eisenhower’s Modern Republicanism?
Truman’s Fair Deal focused on expanding social welfare programs and economic equality, while Eisenhower’s Modern Republicanism prioritized economic growth and limited government intervention.
How did Truman’s containment policy differ from Eisenhower’s “New Look”?
Truman’s containment policy aimed to prevent the spread of communism through direct military intervention, while Eisenhower’s “New Look” relied on nuclear deterrence and alliances to contain Soviet expansion.
What factors contributed to Truman’s unpopularity and Eisenhower’s popularity?
Truman’s unpopularity stemmed from the Korean War and economic difficulties, while Eisenhower’s popularity was due to his leadership during World War II, economic prosperity, and focus on consensus-building.